English language is made up of consonants and vowels that work together to create meaningful words and sentences. Consonants are the sounds that are produced when the airflow is blocked or partially blocked in the vocal tract. In this article, we will explore the different types of consonants in English grammar and their functions.
Types of Consonants
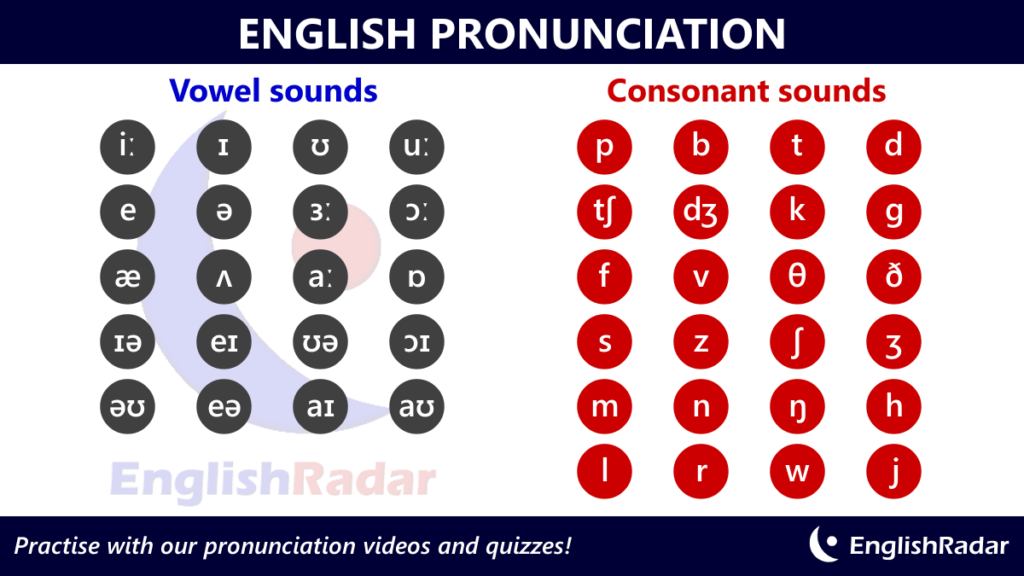
There are two main types of consonants in English grammar: voiced and voiceless. Voiced consonants are produced when the vocal cords vibrate, while voiceless consonants are produced when the vocal cords do not vibrate.
There are also several subcategories of consonants, including plosives, fricatives, affricates, nasals, and liquids. Let's take a closer look at each of these subcategories.
Plosives

Plosives are consonant sounds that are produced by completely blocking the airflow and then releasing it suddenly. Examples of plosives in English include /p/, /b/, /t/, /d/, /k/, and /g/.
Plosives are often described as explosive sounds because of the sudden release of air. They are also sometimes referred to as stops because of the complete stopping of the airflow.
Fricatives

Fricatives are consonant sounds that are produced by partially blocking the airflow and then forcing it through a narrow opening. Examples of fricatives in English include /f/, /v/, /s/, /z/, /ʃ/, and /ʒ/.
Fricatives are often described as hissing or buzzing sounds because of the way the airflow is forced through a narrow opening. They are also sometimes referred to as spirants because of the spiraling airflow.
Affricates
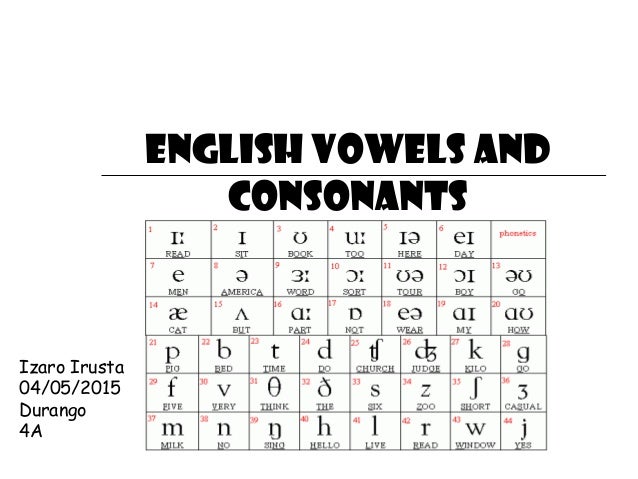
Affricates are consonant sounds that begin as plosives and then transition into fricatives. Examples of affricates in English include /tʃ/ (as in "church") and /dʒ/ (as in "judge").
Affricates are often described as a combination of plosives and fricatives because of the way they transition from one sound to another.
Nasals

Nasals are consonant sounds that are produced by allowing the airflow to pass through the nasal cavity. Examples of nasals in English include /m/, /n/, and /ŋ/ (as in "sing").
Nasals are often described as nasal sounds because of the way the airflow passes through the nasal cavity. They are also sometimes referred to as nasal stops because of the complete stopping of the oral airflow.
Liquids

Liquids are consonant sounds that are produced by allowing the airflow to pass through a partially obstructed vocal tract. Examples of liquids in English include /l/ and /r/.
Liquids are often described as liquid sounds because of the way the airflow passes through a partially obstructed vocal tract. They are also sometimes referred to as semi-vowels because of their vowel-like qualities.
Functions of Consonants

Consonants play several important functions in English grammar, including:
- Making words and sentences more understandable
- Providing rhythm and flow to speech
- Creating emphasis and contrast
- Conveying emotion and tone
Without consonants, it would be difficult to distinguish between different words and to convey meaning effectively in spoken and written communication.
Conclusion
Consonants are an essential part of English grammar, providing the building blocks for meaningful words and sentences. By understanding the different types of consonants and their functions, we can improve our communication skills and become more effective communicators.